By Dr.DAMONMIKI DKHAR (M.V.Sc Cert. Lives. Advisor)
Zoonotic diseases are diseases or infections which are transmitted between animals and man. Zoonotic diseases can be classified according to (i) Etiological/causative agents – caused by virus, bacteria, fungi, parasites, protozoan, rickettsia (ii) Reservior hosts – diseases transmitted from animals to man, man to animals or diseases maintained in both; (iii) Mode of transmission – diseases transmitted from one infected host to another host, diseases which require more than one host or by invertebrate hosts.
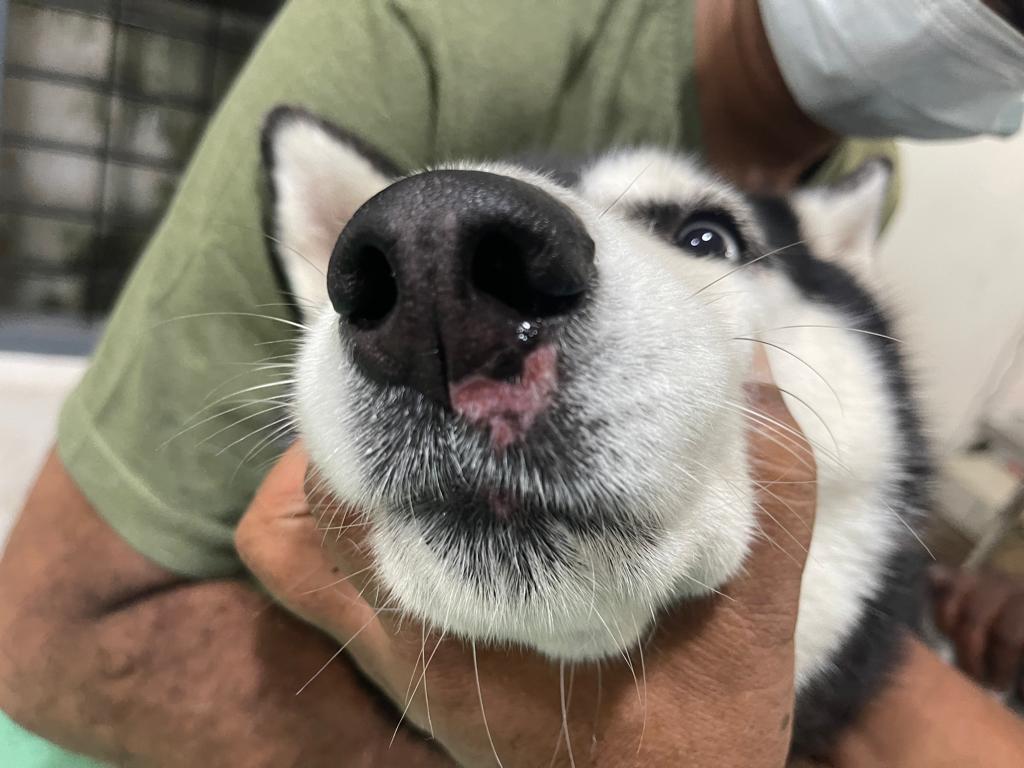
Some examples of Zoonotic diseases of dogs and cats are : Viral – Rabies, Nipah virus infection; Bacterial – Plague, Cat Scratch fever, Lyme disease, Tuberculosis, Salmonellosis, Leptospirosis, Listeriosis; Rickettsial – Q-fever, Rocky Mountain Spotted fever, Ehrlichiosis; Mycotic – Candidiasis, Ringworm, Histoplasmosis, Aspergillosis; Protozoan – Amoebiasis, Giardiasis, Toxoplasmosis; Helminthic – Dipylidiosis, Larva migrans, Toxocariosis, Ancylostomasis, Echinococcis; Ectoparasitic – Scabies.
Zoonoses can be contracted through direct contact, ingestion, inhalation of zoonotic agents, bites from animals and arthropods (vectors), skin wound. Pet owners and handlers are also at high risk of contracting the zoonotic diseases of pets. Healthy pets lead to healthy pet owners.
Control measures for Zoonotic diseases of pets:
1) Practice excellent hygiene when handling pets. Cleaning and washing of hands after being around pets with soap and clean running water and before eating and avoid hand to mouth contact directly after handling pets. Alcohol based sanitizers (with at least 60% alcohol) to be kept at all times for maintaining hygiene with hand washing facilities be made available at pets clinics, hospitals and environment of pets.
2) Eating and drinking to be avoided at places where people contact pets. Proper cooking of all foods of animal origin and handle food safely during food preparation. Thoroughly washing of vegetables and fruits before eating. Drinking water should be boiled, filtered and treated to eliminate water borne zoonoses.
3) Prevent bites from ticks, lice, fleas, mosquitoes. Avoid bites and scratches from animals. Nails and claws of pets should be clipped short and avoid rough play with pets to decrease risk of scratches.
4) Regular disinfection and sanitization of pets house, shelters, cages, kennels, pets utensils, feeders and waterers, etc. with appropriate disinfectants by using gloves from time to time and to prevent accumulation of debris that can shelter microbes and to follow strict sanitary measures.
5) Wearing gloves, facemasks, protective outwears when handling sick pets, when gardening, during daily cleaning of litter boxes especially pregnant women and immune compromised members to decrease risk of Toxoplasmosis.
6) Appropriate disposal of infectious materials, isolation units for pets with known zoonoses and avoiding contact of the same. Regular manure/pets dropping composting and disinfection of litter boxes to be followed. Avoid direct contact with faeces.
7) Avoid dust inhalation and tasting dirt (Risky behaviours) especially inside pets environment.
8) Regular cleaning of aquariums by healthy members (to prevent from Mycobacterium marinum) and avoidance of stray and wild life, non-human primates, animals with diarrhoea/illness is important. Avoid contact with exotic pets including duck and ducklings especially by immune compromised members which spread Salmonella.
9) Avoid feeding of raw foods (meat, fish, eggs), decomposed; left over foods to pets. Garbage and stool eating by pets to be avoided. Don’t allow dogs and cats to hunt. Provision of clean drinking water to pets at all times and don’t allow pets to drink non-potable water.

10) Follow regular vaccination schedule for pets at all costs such as Anti-Rabies, Anti-DHPPi/Lepto, Anti-CRP, Anti-canine corona, Anti-KC, etc. which prevent many zoonotic diseases and worms control (Against round worms, tape worms, hook worms, whip worms, heart worms, etc.) in pets.
11) Adopt regular flea, mite, lice and tick control measures (Vector control) for pets and avoid mosquitoes and flies bites to pets.
12) Regular check-up of pets with periodic testing/screening of parasites and other diseases. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of clinical cases of sick pets (Prophylaxis). Make sure that pets are up to date on their vaccination, deworming and other preventive care.
13) Vaccines for humans/pet owners for few diseases (available) such as Pre-exposure vaccination against rabies and tetanus to pet owners/handlers. Regular worms control for pet owners.
14) Counselling immune compromised pet owners about/ between risks from zoonoses and acknowledgement of human–animal bond and psychological benefits of animal companionship. Children (below 5yrs) and adults (above 65yrs) should be closely supervised when they handle pets especially sick pets as their immune system become vulnerable to zoonotic agents.
15) Detailed zoonoses control measures and guidelines on zoonoses prevention to be made aware and followed by pet owners and Health workers. Be aware of zoonotic diseases at home, school, clinic and outside.